Unveiling Barnard's Star: The Fastest Celestial Traveler
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Barnard's Star
Barnard’s star, one of the nearest stellar neighbors, lies at a distance of less than 6 light-years from Earth, making it the third closest star to our planet, following the Sun and Proxima Centauri. Despite this proximity, many secrets about Barnard’s star have puzzled astronomers for years. Recent advancements, however, have begun to unveil some of these enigmas.
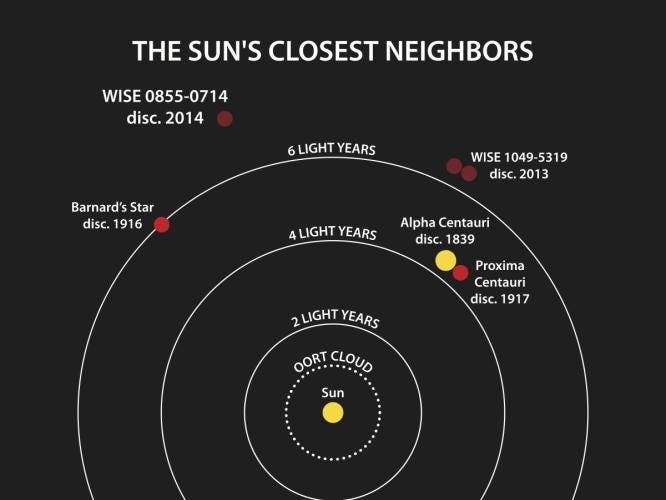
Section 1.1: The Speed of Barnard's Star
One of the most captivating aspects of Barnard’s star is its record as the fastest star in our galaxy, moving at an astonishing speed of approximately 500,000 kilometers per hour. At this remarkable pace, it could traverse the distance from Earth to the Moon in under two minutes.
But what accounts for this extraordinary speed? For a long time, this question lingered unanswered. Some astronomers theorized that Barnard’s star might be undergoing a phase of hyperactivity, propelling it forward. Others speculated that its velocity could be influenced by the gravitational forces of nearby massive objects, such as black holes or other stars.

Section 1.2: Unraveling the Mystery
In 2018, a collaborative team of astronomers from Spain, the UK, and Germany, utilizing a telescope in Chile, made significant progress in understanding Barnard’s star. They concluded that its speed is linked to the movement of the entire Milky Way galaxy instead of local gravitational influences. Their research revealed that Barnard’s star travels at 142 kilometers per second relative to the galaxy's center, a notably high velocity compared to the average star in our galaxy. This finding suggests that Barnard's star has a hyperbolic trajectory, indicating it is moving too quickly to remain in orbit around the galactic center.

Section 1.3: The Cosmic Journey of Barnard's Star
The peculiar movement of Barnard’s star can be traced back to its origins in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy situated on the outskirts of the Milky Way. During a cosmic interaction between the two galaxies, Barnard’s star was ejected from the Large Magellanic Cloud Nebula and embarked on a journey through intergalactic space before entering our galaxy.
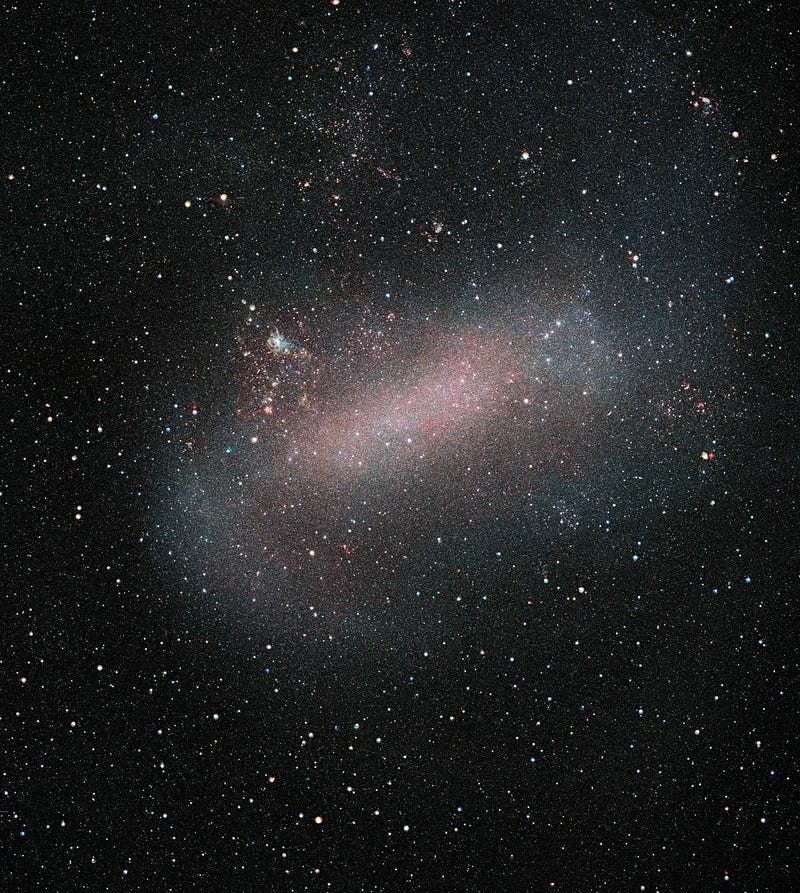

Chapter 2: The Scientific Significance of Barnard's Star
The exploration of Barnard’s star holds significant value in the field of science. Firstly, it enhances our understanding of the origins and evolution of the Milky Way, as well as the dynamics of galaxy interactions. Secondly, Barnard’s star is a prime candidate in the search for exoplanets. Although no planets have been confirmed around Barnard’s star yet, its proximity and rapid movement make it an exciting target for future investigations.
The first video titled "Barnard's Runaway Star - Fastest Moving Star in the Sky" delves into the fascinating characteristics and significance of Barnard's star, shedding light on its remarkable speed and the implications for our understanding of stellar motion.
The second video, "Your Sky Tonight - The Super-Earth Around Barnard's Star," discusses the potential for discovering planets in the vicinity of this intriguing star, exploring the ongoing research and future possibilities for exoplanet detection.
In summary, Barnard’s star remains one of the most intriguing celestial objects in our galaxy. Its incredible speed and unique origin from the Large Magellanic Cloud offer valuable insights into cosmic processes, paving the way for new discoveries in astronomy. The star stands as a potential beacon for future exoplanet searches, which could reshape our understanding of life beyond Earth.
Don't forget to clap if you're interested in more articles about space! Subscribe to our channel and feel free to ask your questions; I will address them in future articles.