Mastering Self-Learning: Effective Strategies for Growth
Written on
Understanding Your Learning Style
To enhance your study habits, it's essential to recognize your unique learning style. This allows for the development of a tailored learning approach that suits you best. Learning styles can be categorized as follows:
- Visual: Learners who grasp concepts better through images and diagrams.
- Auditory: Those who retain information by listening and verbalizing.
- Reading/Writing: Individuals who learn effectively through text and written materials.
- Kinesthetic: Learners who understand concepts by engaging in hands-on activities.
Identifying your preferred learning style enables you to adopt techniques that will optimize your learning experience. For instance, a kinesthetic learner might benefit from physically disassembling a clock to understand its mechanics, while a visual learner may prefer to study a diagram illustrating the clock's functions. Similarly, someone with a reading/writing preference could read an informative article about clocks, while an auditory learner might listen to a lecture on the topic.
Understanding your learning style is crucial; it helps you select resources that cater to your strengths in self-directed learning. If you're unsure of your learning style, consider taking an online self-assessment, such as:
What's Your Learning Style? 20 Questions
Auditory If you are an auditory learner, you learn by hearing and listening. You understand and remember things you…
www.educationplanner.org
Setting Clear Learning Goals
Establishing specific learning objectives is vital for effective self-directed study. Without clear goals, your learning sessions may lack direction and purpose. Here’s how to structure your learning goals:
- Identify the Main Goal: Write your primary learning objective in the center of a page.
- Break Down into Sub-Goals: Divide your main goal into smaller, manageable objectives. For example, if you aim to memorize 100 words for an English exam, you might set a goal of learning five related words in each session. This approach creates a flexible plan for your studies.
- Include Review Sessions: Incorporate regular reviews of previously learned material to reinforce retention. For instance, start each new session by revisiting the last five words you learned.
- Set Weekly Feedback Objectives: Dedicate time each week to assess your progress and reflect on your learning.
As you embark on your study journey, remember to pace yourself. Begin with study sessions lasting between 20 to 50 minutes, depending on your concentration levels. Take 10-minute breaks to enhance productivity, and avoid studying for more than two continuous hours without a break.
The Importance of Self-Discipline
Self-discipline plays a critical role in reaching your educational goals. Maintaining focus and commitment requires a certain standard of discipline. To cultivate effective self-discipline, consider the following strategies:
- Create a Structured Plan: Schedule important tasks in your calendar.
- Take Immediate Action: Begin your study sessions promptly to gauge your progress.
- Optimize Your Study Environment: Minimize distractions to maintain concentration.
- Hold Yourself Accountable: Regularly evaluate your actions and commitments.
While personal discipline may seem challenging, the rewards are significant. You will likely find greater concentration and fulfillment in your self-learning journey.
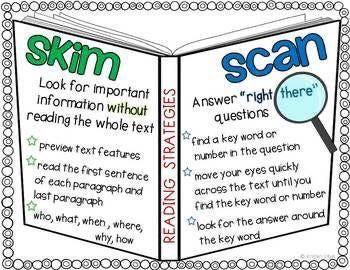
Effective Reading Strategies
To read efficiently, employ the skimming and scanning techniques:
- Skim: Initially, glance through the text to identify keywords, main ideas, and repeated themes. This initial review helps you grasp the overall context.
- Scan: For specific information, quickly search through the text for keywords or numbers. This method allows you to find answers to critical questions about the content.
As you read, consider creating visual aids to help you remember concepts, particularly if you're a visual learner. For instance, when studying poetry, you might illustrate connections between themes or lines.

Note-Taking Techniques
Taking notes is an active process that helps solidify your understanding of the material. Here’s how to make the most of your note-taking:
- Jot down brief reflections as you read, marking any passages that confuse you.
- Use symbols or keywords in the margins to capture your thoughts on key concepts.
- If a particular section is challenging, reread it, focusing on the meanings of individual sentences.
Consider keeping a dedicated notebook for your notes, allowing for easy reference later. This practice can enhance your comprehension and retention of the material.
Final Reflections and Continuous Improvement
Creating a personal knowledge base is essential for retaining the information you acquire. This can include:
- Inspirational quotes
- Notes from books and articles
- Personal development tips
- Goals and achievements
Regularly reviewing this knowledge base can boost your learning efficiency and help you stay organized.
Lastly, take time to evaluate your learning process. Reflect on what strategies worked well and what didn't. This self-assessment, known as metacognition, enables you to adapt and improve your learning techniques. Keep in mind that progress takes time, and the combination of patience, perseverance, and diligence will ultimately lead to success.
"Patience, perseverance, and hard work are a unique combination for success."
— Napoleon Hill