Innovative Hookworm Research: A New Era in Drug Delivery
Written on
Chapter 1: The Unlikely Heroes of Medicine
Worms often evoke a sense of discomfort among many, yet they play essential roles in various ecosystems. Among these, hookworms present a unique case; these intestinal parasites thrive by using humans as hosts. Typically, they enter the body either through ingestion or by penetrating the skin when individuals walk barefoot on contaminated ground. The likelihood of hookworm infection rises in warm, humid regions lacking adequate sanitation. Soil contamination often occurs when human waste is improperly managed or used as fertilizer.
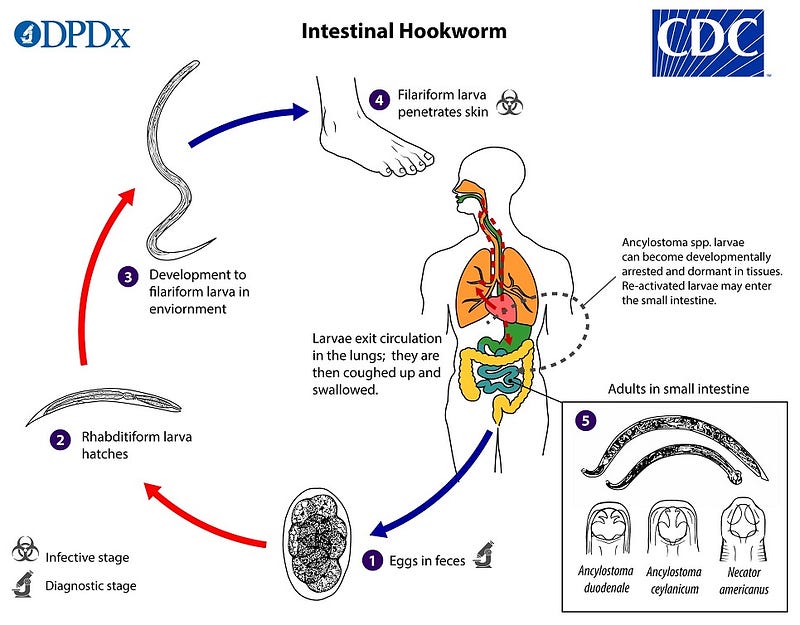
The lifecycle of intestinal hookworms, particularly A. duodenale and N. americanus, demonstrates their adaptability. Notably, A. duodenale can remain dormant within the host's muscles or intestines, leading to new infections. Common symptoms include localized rashes, abdominal discomfort, and fatigue, with children being especially vulnerable due to potential impacts on their growth and development. While modern medicine effectively treats these infections, the CDC estimates that between 576 and 740 million people worldwide are currently infected.
Section 1.1: Scientific Innovation Inspired by Nature
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University are turning the hookworm's characteristics into a source of inspiration for new medical advancements.
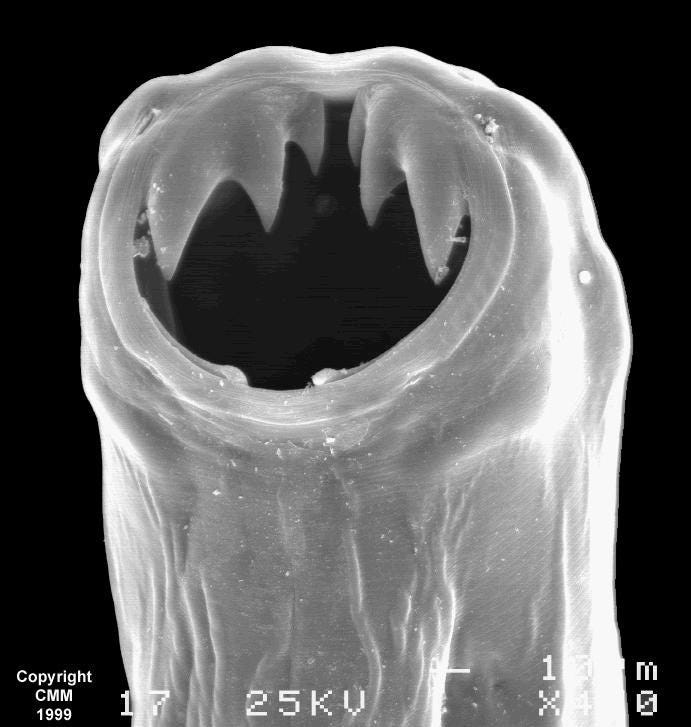
Collaborating on this groundbreaking project, Dr. Florin M. Selaru and Dr. David Gracias have published their findings in the October issue of Science Advances. Their research explores the hookworm's mouth and teeth to create innovative drug delivery devices called theragrippers. These tiny devices, nearly invisible to the naked eye, feature sharp microtips designed to attach to the innermost intestinal layer, known as the mucosa.
Subsection 1.1.1: Mechanism of Theragrippers
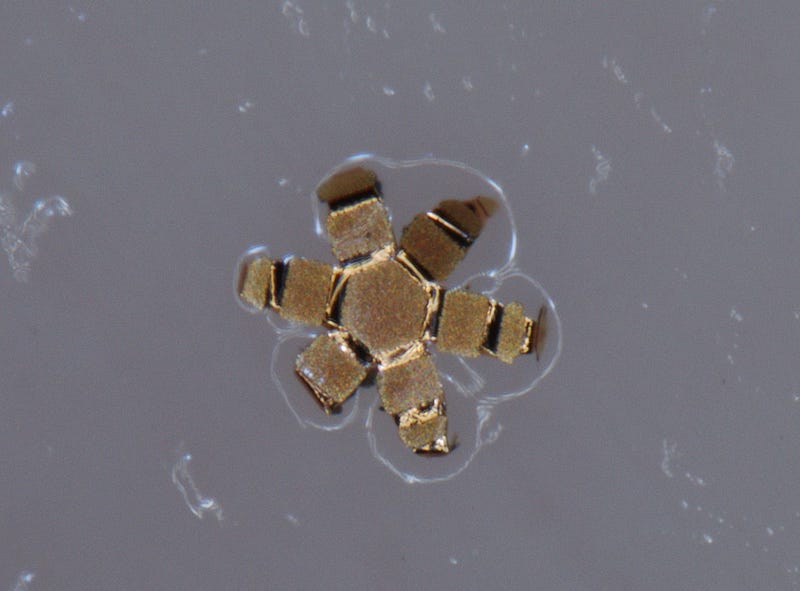

Constructed from biocompatible materials like gold and chromium, theragrippers have shown no adverse reactions in animal studies. As noted by Dr. Arijit Ghosh, the first author of the study, future designs aim to extend the device's retention time in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to several days.
The initial tests conducted on rats and pigs revealed that theragrippers could remain in the GI tract for approximately 24 hours, significantly improving the exposure and absorption of the model drug ketorolac, a pain relief medication commonly used post-surgery.
Section 1.2: Ensuring Targeted Delivery
A crucial question arises: how can doctors ensure theragrippers remain in the desired location? Dr. Selaru suggests using existing oral medication capsules designed to withstand stomach acidity, allowing for targeted delivery of thousands of theragrippers into the intestines.
The study also addresses the issue of inconsistent adherence to prescribed medication regimens, which leads to an estimated $600 billion in waste annually. By creating a more efficient drug delivery system, the team aims to enhance prescription adherence while reducing waste, representing a significant advancement in biotechnology.
Chapter 2: The Intersection of Nature and Innovation
This research exemplifies how nature can inspire innovative solutions to human challenges. Dr. Selaru reflects on the process of discovery, likening it to an accumulation of experiences that eventually lead to breakthroughs.
While this revolutionary technology is still years away from practical application, it holds promise for the future of drug delivery. Thorough clinical trials must be conducted before it can be approved by the FDA, yet the potential impact of this research is undeniably exciting. For those interested, a detailed examination of the study can be found in the full article published in Science Advances.
Interested in discussing advancements in biotechnology or bioeconomy? Connect with us! If you’re working on innovative science that contributes to this dialogue, leave a comment below. Don’t miss our other fascinating articles:
Bacteriophages: Harnessing Viruses to Save Lives
SARS-CoV-2 has been a global pandemic since March 2020. Scientists have been working tirelessly to find solutions.
Follow Bioeconomy.XYZ to discover more about how biotechnology is reshaping our world.