The Benefits of Biodiversity in the Workplace for Health
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Workplace Biodiversity
This section introduces the concept of biodiversity within work environments and its potential to enhance employee well-being and organizational success while also benefiting the planet.
Previously, I discussed how nature-inspired solutions can transform environmental, social, and economic hurdles into innovative opportunities. I also examined the Planetary Health framework, which views human and environmental wellness as interconnected systems. By fostering biodiversity, workplaces—including the companies, employees, and communities within them—can significantly contribute to the transformation of planetary health.
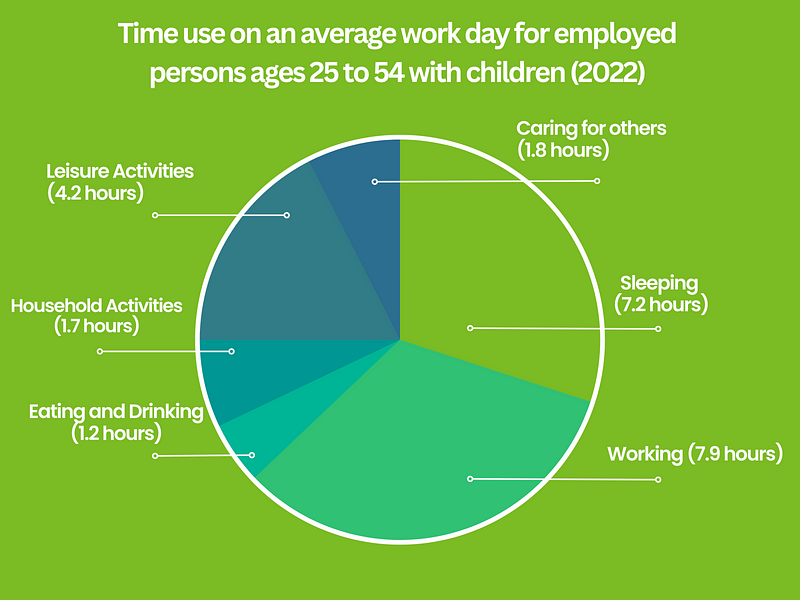
Statistics indicate that the average American spends about eight hours at work each day, as reported by the 2022 American Time Use Survey. This is nearly double the time spent on leisure activities, like watching television or engaging in sports. Compared to two decades ago, individuals are now dedicating more time to work-related tasks, whether they are in part-time or full-time roles.
A Gallup survey involving 16,000 working adults in the U.S. revealed that about 20% of employees assess their mental health as "fair" or "poor." This decline in mental health also hampers the economy, with affected employees taking an average of 12 unplanned sick days per year, compared to only 2.5 days for those with good mental health. Collectively, poor mental health in the workplace costs the economy nearly $48 billion each year due to lost productivity.
Biodiversity encompasses the variety of species, habitats, and genetic diversity within each species. Approximately 9 million types of plants, animals, fungi, and protists populate our planet. However, the 7 billion human residents are threatening these ecosystems. A 2019 report, based on a thorough review of 15,000 scientific and governmental sources, found that nearly 1 million species face extinction. The swift decline of biodiversity has far-reaching implications across various societal sectors, including economic and workplace contexts.
The World Bank forecasts that deteriorating ecosystems could impose a $2.7 trillion annual cost on the global economy by 2030—just seven years away. Over half of the global GDP ($44 trillion) is "moderately or highly dependent" on nature and its services. Consequently, the loss of biodiversity is projected to cost the global economy more than $5 trillion annually in diminished natural services.
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in human health. We rely on ecosystem services—such as fresh water, food, and energy sources—and individuals residing in biodiverse settings report higher levels of positivity. Metrics like species richness can indicate the ecological health of an area. Research indicates that ecologically beneficial landscapes can enhance mental health and overall well-being; even small encounters with nature can uplift mood, sharpen focus, and foster social trust and cohesion. In workplace environments, this translates to enhanced employee well-being, improved productivity, and a positive company culture.
Chapter 2: The Work and Biodiversity Series
Introducing the Work and Biodiversity Series for Symbiotica, we recognize that corporate functions depend on thriving ecosystems and biodiversity. Despite this, only a minority of companies globally have established climate change objectives, and even fewer focus on promoting or protecting biodiversity. While the exact impact of robust environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices on financial performance remains uncertain, "green initiatives" could provide sustainable solutions to various challenges. These practices might also grant businesses a competitive edge, foster positive long-term relationships with customers, and enhance employee recruitment and retention.
Addressing climate change and biodiversity loss necessitates a transformative approach at the systems level. Collaboration with policymakers and practice stakeholders is essential for tackling these issues in a holistic and systematic manner, thereby generating multi-faceted solutions.
The insights, opportunities, challenges, and success stories presented by Symbiotica in this series are designed to be small but scalable. Our focus will not be on carbon offsets or payments for ecosystem services; instead, we will emphasize actionable steps that even the smallest business or entry-level employee can take to make a difference.
Given that workplace stress is a significant contributor to mental health issues, it is increasingly crucial to understand how promoting biodiversity in work settings can enhance well-being. By implementing simple and cost-effective measures, we can simultaneously support both our health and the environment.
Why Biodiversity Matters
This video delves into the importance of biodiversity, explaining its essential role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and supporting human life.
The Importance of Biodiversity Conservation
This video discusses why conserving biodiversity is critical for the planet, exploring the implications of biodiversity loss and the measures needed to protect it.