Understanding Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life's Processes
Written on
Chapter 1: The Essential Role of Enzymes
Enzymes are fundamental to life, and though you might recall them from high school biology, they are much more than just a trivia answer. These vital compounds are integral to our existence, serving as the driving force behind the biological processes that sustain us.
What Are Enzymes?
At their core, enzymes are biological catalysts. This definition may sound circular, but it highlights their purpose rather than their structure. Enzymes are crucial substances that help living organisms perform necessary chemical transformations more efficiently.
Consider a biological cell as a ship that is continually facing challenges, much like one caught in a storm. The ship remains afloat only as long as its crew manages repairs. Similarly, cells are in a constant state of repair to combat the forces of entropy, which threaten their integrity. Without constant maintenance, cell membranes would deteriorate, and organelles would malfunction, ultimately leading to cellular collapse.
But the functions of cells extend beyond mere repairs. They are capable of linking peptide chains to create proteins and constructing phospholipid membranes. They can even reproduce themselves at a molecular level, akin to constructing a building using bricks. Enzymes facilitate all of these processes. While DNA serves as the blueprint for life, enzymes execute the construction.
Enzymes as Tools
Like skilled artisans, cells require a diverse array of tools for construction and maintenance, and enzymes fulfill this role. They are responsible for binding molecules together or breaking them apart, as well as modifying them in various ways. But how do enzymes achieve these complex tasks?
How Enzymes Function
Let’s first examine chemical reactions. For instance, when an oxygen atom is added to a carbohydrate, both entities undergo a transformation—this is a chemical reaction. Common types of reactions include synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement.
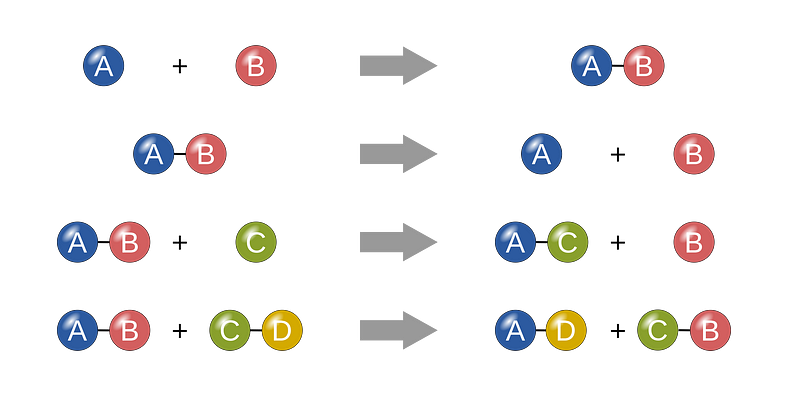
Enzymes simplify these processes. To illustrate, imagine attempting to saw a wooden board in half. If you hold it with one hand, achieving a clean cut is challenging. However, if you secure the board on two stable surfaces, the cutting process becomes straightforward. In enzyme activity, it is crucial to stabilize a molecule during reactions. Molecules tend to vibrate and move, complicating the reaction process. Enzymes help by holding these molecules in place, optimizing them for reactions to occur.
For example, consider the difficulty of cutting a bond between atoms without proper stabilization. Enzymes create a "template" for reactions, ensuring that substrates are held in an ideal position for transformation.
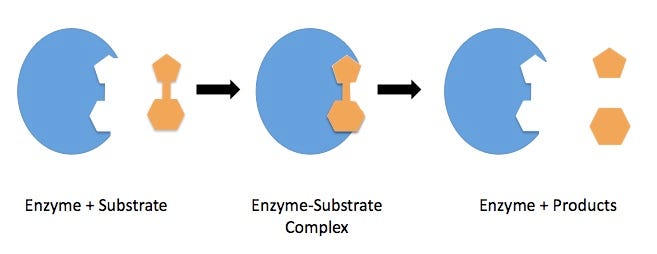
One key question arises: how does an enzyme know when to release a product? The answer lies in its shape. Enzymes are flexible and can undergo conformational changes in response to their environment. When a reaction completes, the product differs from the initial substrate, prompting the enzyme to change shape and release the product, thus preparing for the next substrate.
Specialization of Enzymes
Contrary to what one might assume, each enzyme is specialized for a specific task. The active site of an enzyme is uniquely shaped to accommodate only particular substrates. Environmental factors such as temperature and pH can affect enzyme functionality, sometimes permanently.
Enzymes exhibit further specialization; different enzymes can act on the same molecule in distinct ways. For instance, glucose dehydrogenase removes hydrogens from glucose, while hexokinase adds a phosphate group. The variety of enzymes is immense, and they are typically named with the suffix "-ase," often reflecting the molecules they act upon.
Chains of Reactions
Understanding how individual enzymes operate allows us to appreciate how they can work in concert to facilitate cellular processes. For example, a glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme may generate glucose, which can then be acted upon by glucose oxidase. Enzymes collectively modify molecules, enabling the cell to perform necessary functions.
Cells can also regulate enzyme activity in response to environmental changes and signaling molecules. Some enzymes manage their own regulation through feedback mechanisms, forming the foundation of a cell's control network. This allows cells to maintain integrity and replicate or construct new structures as needed.
The first video titled "What are enzymes?" provides a straightforward overview of these essential biological catalysts.
The second video, "What are Enzymes?", delves deeper into the role of enzymes in various biological processes.
References
- Enzymes: Function, definition, and examples. Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the body. They affect every function, from breathing to digestion. [Read more](www.medicalnewstoday.com)
- Enzymes: What Are Enzymes, Pancreas, Digestion & Liver Function. Enzymes are proteins that help speed up metabolism, or the chemical reactions in our bodies. [Read more](my.clevelandclinic.org)
- Enzyme Conformation. Enzymes are biomolecules of particular interest, as they have high substrate specificity and exhibit high catalytic activity. [Read more](www.sciencedirect.com)