Futuristic Chip Design: The Dawn of Adaptive Transistors
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Advanced Transistor Technology
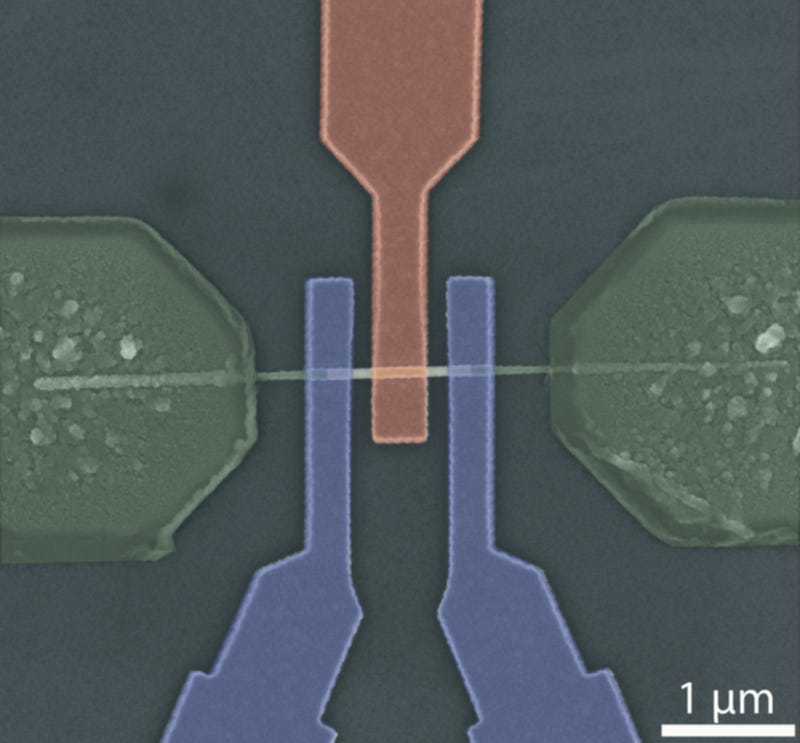
The landscape of electronics is on the brink of transformation with the introduction of adaptive transistors. Unlike traditional chips, which often face limitations in functionality, the latest designs incorporate a dual-gate system — a control gate (red) and a program gate (blue) — allowing for unprecedented flexibility in performing a variety of logical operations.
As we transition into an increasingly digital world, semiconductor chips have emerged as vital components in all electronic devices. The recent pandemic-induced supply chain disruptions have underscored this significance, leading to a notable chip shortage that has affected manufacturers and consumers alike. While these supply issues are expected to improve over time, the pace of chip innovation is accelerating. Major players like Intel, Nvidia, and IBM are at the forefront of these advancements.
Section 1.1: The Shift from Fixed to Flexible Functionality
In a groundbreaking development, researchers recently unveiled the first silicon chip employing a universal decoding algorithm. For years, efforts have concentrated on creating chips with fixed functionalities, aiming to increase the number of transistors within a given area. However, this focus has reached a physical limit, prompting a search for more versatile solutions.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Role of Adaptive Transistors
The future lies in the creation of adaptive transistors that can be quickly reconfigured to perform different logical tasks as needed. This innovation not only opens new possibilities for chip design but also paves the way for advancements in artificial intelligence, neural networks, and multi-valued logic systems.
The first video titled "Amplify Science Traits and Reproduction 1.2 - YouTube" provides an insightful overview of how adaptive transistors function and their implications for future technology.
Section 1.2: Innovations in Transistor Materials
At TU Wien in Vienna, scientists have developed the world's most flexible transistor by utilizing germanium instead of traditional silicon. This new prototype leverages the unique properties of germanium alongside specialized program gate electrodes, signaling a potential shift in chip technology.

According to Prof. Walter Weber, the team lead, “Previously, the intelligence of electronic devices stemmed from connecting multiple transistors with limited functionality. The new transistor's adaptability marks a significant advancement in electronics.”

The transport of electric charge in this innovative transistor relies on both electrons and "holes," the latter being missing electrons that carry a positive charge. The TU Wien design manipulates both types of charge carriers simultaneously, enhancing efficiency and functionality.
Chapter 2: Practical Applications and Future Implications
The new transistor features an extremely thin germanium wire connecting two electrodes, incorporating a unique, clean interface with metal on both ends. In addition to the standard gate electrode, there is another control electrode that dynamically adjusts the transistor's function.
The second video titled "Amplify Science Traits and Reproduction 1.3 - YouTube" explores potential applications of this technology in artificial intelligence and beyond.
This dynamic control allows for the customization of the transistor's properties, enabling it to switch between functions like a NAND gate and a NOR gate with ease. What previously required 160 transistors can now be achieved with just 24, drastically improving speed and energy efficiency.
Researchers anticipate that this innovative technology could lead to commercial applications without necessitating new manufacturing processes, as the materials are already readily available. The potential use cases in artificial intelligence, where circuits can be adjusted on the chip itself, are particularly exciting. The full research findings are documented in the Journal of ACS Nano.
Stay connected for more updates on this revolutionary technology.