How Carbon Nanotubes Could Revolutionize Solar Energy Efficiency
Written on
Chapter 1: The Solar Landscape
Currently residing in Phoenix, AZ, one of the hottest cities in the U.S., I’m considering purchasing a home. The summer temperatures can soar to 120 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees Celsius), making solar energy an appealing option. My goal is to install solar panels to harness the abundant sunlight throughout the year, contributing to environmental sustainability and lowering my electricity expenses. Solar panels, once seen as costly and impractical, have become more accessible due to significant technological advancements, particularly in nanotechnology, which can enhance their efficiency. Let’s delve deeper into this fascinating subject!
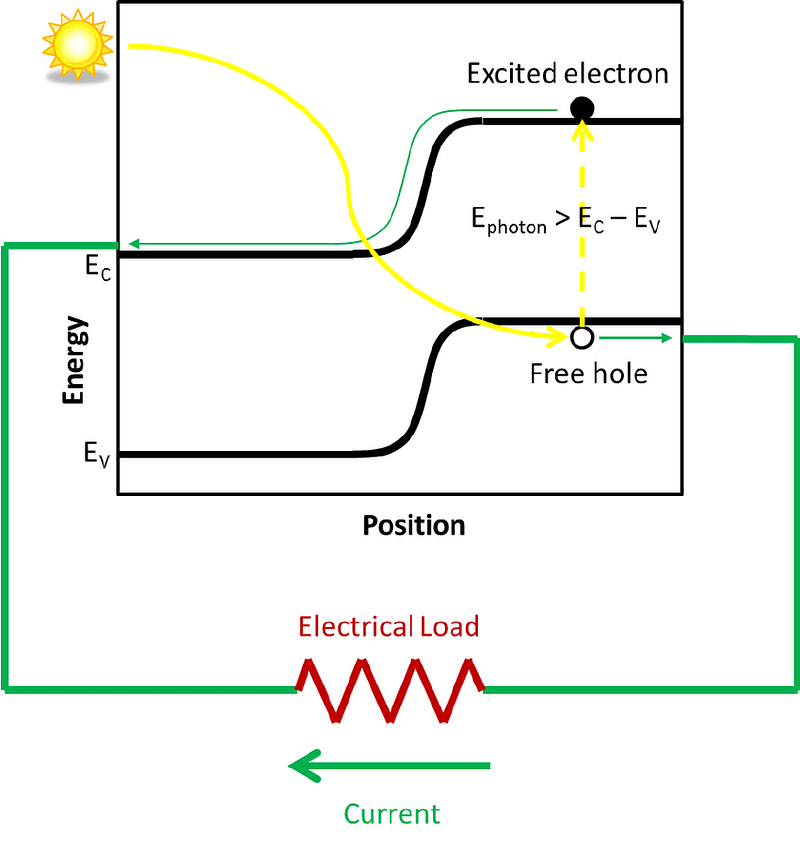
Understanding Solar Cell Mechanics
To appreciate how nanotechnology can enhance solar panel efficiency, it's essential to understand the mechanics of silicon solar panels, which constitute about 95% of the market today. Silicon, a semiconductor, houses electrons in high-energy states within the valence band. The conduction band above it allows electrons to flow freely once they gain sufficient energy, such as from sunlight.
When sunlight strikes the panel, electrons can absorb photons and jump from the valence band to the conduction band. This movement of electrons creates an electric current, powering various devices connected to the solar panels.
The Limitations of Conventional Solar Cells
Despite their utility, solar cells have an inherent efficiency ceiling. In 1961, physicists William Shockley and Hans-Joachim Queisser established that single silicon solar cells could only theoretically convert about 30% of sunlight into electricity. Over the years, various methods have been developed to exceed this limit.

Innovations with Carbon Nanotubes
In 2019, a team led by Junichiro Kono at Rice University unveiled a groundbreaking innovation: integrating carbon nanotube arrays with silicon solar cells to potentially boost efficiency to around 80%. This advancement hinges on the ability of carbon nanotubes to transform thermal photons emitted by the solar cells into a form that can be efficiently converted into electricity.
When solar cells absorb sunlight, they emit thermal photons in a broad spectrum. However, for optimal energy conversion, they require narrowband light. Kono’s research indicates that carbon nanotubes can facilitate this conversion, capturing wasted infrared light and transforming it into usable electricity.
Future Prospects
The initial excitement surrounding carbon nanotubes was immense, with some envisioning their use in constructing a space elevator. Although the hype has subsided, ongoing research suggests that the solar industry may soon benefit significantly from these materials. Could carbon nanotubes be the key to unlocking the next generation of solar technology?
If you found this discussion enlightening, consider exploring these related topics:
- What Is Nanotechnology and Its Current Applications? — A brief history of nanotechnology.
- Unlocking New Technologies at the Nanoscale — Insights into the unique advantages of working at this scale.
- Scientific Approaches to Contacting Extraterrestrial Life — Various methods explored by scientists.
Citations:
Boysen, Earl, and Nancy C. Muir. Nanotechnology for Dummies. Wiley & Sons, 2011.